LeetCode 04 : Container With Most Water
Problem
You are given an integer array height of length n. There are n vertical lines drawn such that the two endpoints of the ith line are (i, 0) and (i, height[i]).
Find two lines that together with the x-axis form a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Return the maximum amount of water a container can store.
Notice that you may not slant the container.
Example 1:
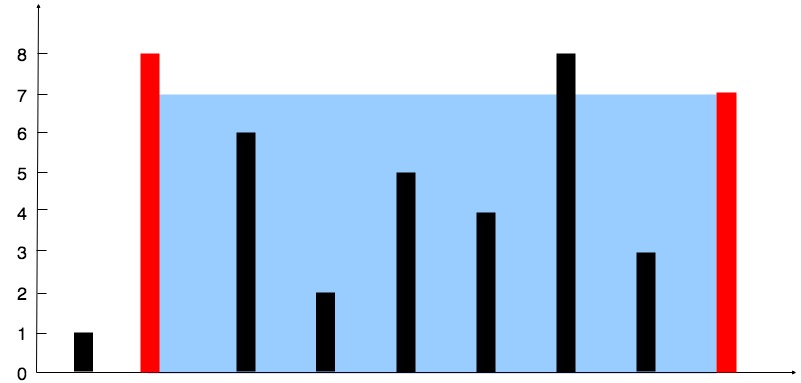
Input: height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
Output: 49
Explanation: The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example 2:
Input: height = [1,1]
Output: 1
Constraints
- n == height.length
- 2 <= n <= 105
- 0 <= height[i] <= 10^4
Solution
class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] heights) {
int maxArea = 0, p1 = 0, p2 = heights.length -1 ;
while ( p2 > p1 ) {
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, Math.min(heights[p1],heights[p2]) * Math.abs(p2 - p1));
if(heights[p1] <= heights[p2]){
p1++;
} else {
p2--;
}
}
return maxArea;
}
}
The above solution is for the "Container With Most Water" problem using the two-pointer approach to find the maximum amount of water a container can store between vertical lines. Here's how the code works:
- The
maxAreafunction takes an integer arrayheightsas input and returns an integer representing the maximum amount of water a container can store. - It initializes variables
maxAreato store the maximum area andp1andp2as pointers to track the left and right vertical lines. - The loop iterates while
p2is greater thanp1, indicating there are still possible combinations of lines to check. - Inside the loop:
- The current area is calculated as the minimum height between the lines at positions
p1andp2, multiplied by the width between them (Math.abs(p2 - p1)). - The maximum area is updated using
Math.max. - If the height at
p1is less than or equal to the height atp2, it means moving the left pointer (p1) inward might lead to a larger area, sop1is incremented. - Otherwise, the right pointer (
p2) is decremented since moving it inward might lead to a larger area.
- The current area is calculated as the minimum height between the lines at positions
- Finally, the maximum area is returned.
The two-pointer approach efficiently searches for the largest possible area by systematically moving the pointers towards each other. This ensures that all possible combinations of lines are considered while avoiding unnecessary computations.
This code provides an effective solution for finding the maximum amount of water that can be stored between vertical lines.
Related Articles
- LeetCode 01 : Two Sum
- LeetCode 02 : Add Two Numbers
- LeetCode 03 : Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
- LeetCode 04 : Container With Most Water
- LeetCode 05 : Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
- LeetCode 06 : Maximum Subarray
- LeetCode 07 : Contains Duplicate
- Codechef 01 : Problem Code: AGELIMIT
- Codechef 02 : Problem Code: BURGERS